3.1.2.2 Feathering
Feathering is a selection edge treatment similar to antialiasing. It
works by changing the alpha value of pixels as a function of their
radial distance from the selection edge.
Figure
3.13
Figure 3.13:
The Effect of Feathering
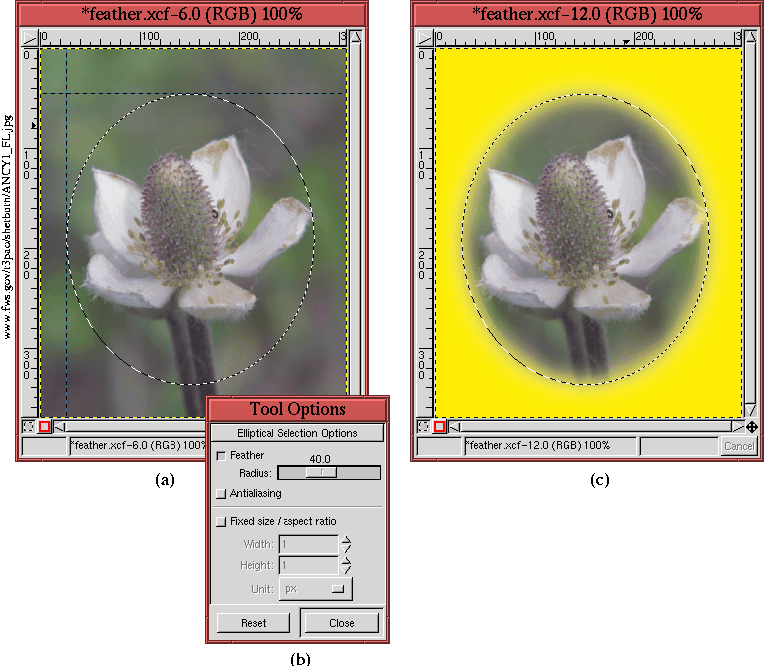 |
illustrates an example of a feathered selection.
Figure
3.13(a) shows how two guides have been
placed to aid in framing a selection using the
Ellipse Select
tool.
As shown in Figure
3.13(b), a value of 40 has
been chosen for the Feather Radius in the Tool Options dialog
for this selection tool. Furthermore, Antialiasing has been turned
off. The result of inverting the selection and cutting away the
background is shown in Figure
3.13(c). This
result is actually displayed on a yellow background so that the
transparency of the flower pixels can be better seen. Also,
superimposed on Figure
3.13(c) is the original
elliptical selection.
The transparency of the flower image shown in
Figure
3.13(c) is 50% at the selection edge.
The transparency increases moving outward from the edge and decreases
moving inward from it. The rate at which the transparency changes
while moving away from the selection edge is determined by the Feather
Radius. For this example, the value chosen is 40, meaning that there
is a feathering effect up to 40 pixels away in both directions from
the selection edge. Note that for all the selection tools, feathering
is off by default.
Partially selected pixels are discussed again in
Section
4.1.7.
