The default GNOME installation includes several applets and applications. This section briefly explains two of the most popular GNOME programs, the GNOME terminal application and the GNOME CD Player applet.
The GNOME terminal application, shown in
Figure 6.8, provides a window in which you can type shell commands and view their output. To launch GNOME terminal, select Utilities  GNOME Terminal from the main menu. You can open multiple GNOME terminal windows if you like.
GNOME Terminal from the main menu. You can open multiple GNOME terminal windows if you like.
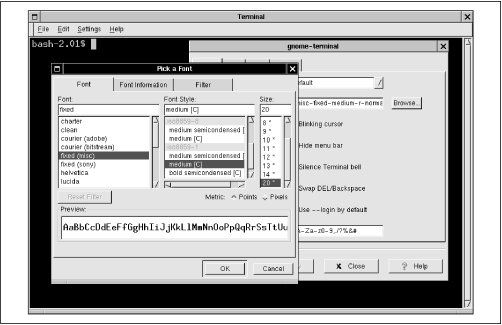
The Settings menu lets you configure the operation of GNOME terminal. For example, you may find that the default font is too large or too small for your liking. If so, select Settings  Preferences from the GNOME terminal window. A dialog box pops up. Select the General tab and left click the Browse button next to the Font field. A second dialog box pops up, from which you can select the font, font style, and font size you prefer.
Preferences from the GNOME terminal window. A dialog box pops up. Select the General tab and left click the Browse button next to the Font field. A second dialog box pops up, from which you can select the font, font style, and font size you prefer.
To exit GNOME terminal, simply type
exit on the command line and press
Enter. Alternatively, select File  Close Terminal from the menu.
Close Terminal from the menu.
Figure 6.9 shows the GNOME CD Player, which is represented by a window on the desktop and an icon on the panel. CD Player lets you play audio CDs though your computer's sound card. However, CD Player won't function unless you have read access to your CD-ROM's device file. If CD Player fails, log in as root and use the following command to give all users read access to the CD-ROM:
chmod a+r /dev/cdrom
This command assumes that the symbolic link
/dev/cdrom correctly refers to your CD-ROM device; if necessary, use a different argument that refers to your CD-ROM device.
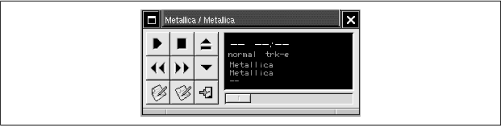
The buttons that operate CD Player resemble those found on other CD Players, such as the one provided with Windows 9x. You can play, stop, or pause the CD Player, eject the CD, fast forward or rewind.
If your computer is connected to the Internet, CD Player can also access the database of CD information help on the CDDB Web site,
https://www.cddb.org/. By doing so, CD Player can determine the artist and title of a CD and the titles of its tracks.
CD Player also lets you open a dialog box that lets you manually edit CD information. This is helpful if your computer is not connected to the Internet or if you find that the information on the CDDB database is incomplete or not to your liking.
