5.6.4 The Darken Only and Lighten Only Blending Modes
Darken Only creates a resultant pixel that retains the smallest
components of the foreground and background pixels. Thus, if the
foreground pixel has the components
[r1,g1,b1] and the background
has
[r2,g2,b2], the resultant pixel is
![$[\min(r_1,r_2),\min(g_1,g_2),\min(b_1,b_2)]$](img183.gif) .
This is expressed more
compactly as
.
This is expressed more
compactly as
where
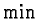
means component-wise minimization. Not surprisingly,
Darken Only mode makes an image darker.
Figure
5.19(a)
Figure 5.19:
An Example of Darken Only and Lighten Only Modes
 |
illustrates the use of
Darken Only mode on the flower image from
Figure
5.15(a). Because the grayscale layer below
the flower is uniformly
127
R 127
G 127
B, everything in the flower
that has an RGB component darker than 127 retains its character in the
image. The parts of the flower image that are lighter are replaced
by the flat gray.
Lighten Only mode has the opposite action of Darken Only.
It selects the maximum of each component from the foreground and
background pixels. The mathematical expression for Lighten Only
is
where
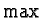
means component-wise maximization.
Lighten Only
mode makes an image lighter.
Figure
5.19(b) illustrates the use of
Lighten Only mode on the flower image from
Figure
5.15(a). Now, everything in the flower
that has an RGB component lighter than 127 retains its character in
the image. The parts of the flower image that are darker are replaced
by the flat gray.
