The
dselect tool provides an easy-to-use,
character-based graphical front-end for accesing
dpkg. To launch
dselect, issue
the command:
dselect
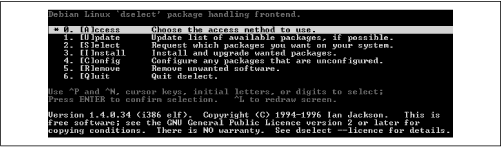
Figure C.2 shows the screen that
appears. The screen presents a simple menu having six items:
-
Access
-
This menu item lets you choose the
method used to access package files.
-
Update
-
This menu item lets you update the list
of available packages.
-
Select
-
This menu item lets you choose packages
for installation or removal.
-
Install
-
This menu item initiates installation of
selected packages.
-
Config
-
This menu item initiates configuration
of installed packages.
-
Remove
-
This menu item initiates removal of
packages selection for removal.
-
Quit
-
This menu item exits
dselect.
The menu items are generally used in the order in which they are
presented.
To choose the access method, use the arrow keys to highlight the
Access menu item and press
Enter. The
screen shown in
Figure C.3
appears.
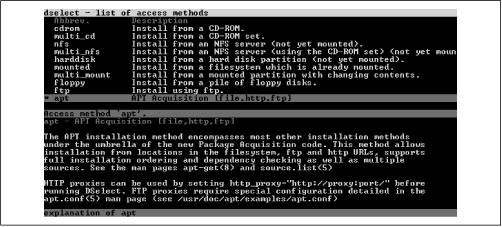
The most flexible access method - and the method that's
generally recommended - is
apt. Other
available options include:
-
cdrom
-
Lets you install packages from a
CD-ROM. This access method has been deprecated; you should use
multi_cd instead.
-
multi_cd
-
Lets you install packages from a
multi-volume set of CD-ROMs.
-
nfs
-
Lets you install packages residing on an
NFS server. This access method has been deprecated; you should use
multi_nfs instead.
-
multi_nfs
-
Lets you install packages residing on an
NFS server that has access to a multi-volume set of packages.
-
harddisk
-
Lets you install packages residing on a
hard disk partition that is not currently mounted. This access method
has been deprecated; you should use
apt or
multi_mount instead.
-
mounted
-
Lets you install packages residing on a
currently mounted filesystem. This access method has been deprecated;
you should use
apt or
multi_mount instead.
-
multi_mount
-
Lets you install packages from a
multi-volume set, one volume of which is currently mounted.
-
floppy
-
Lets you install packages from a set of
floppy diskettes.
-
ftp
-
Lets you install packages residing on an
FTP server.
To choose an access method, use the arrow keys to highlight the
appropriate menu item and press
Enter.
If you selected the
apt access method,
you'll be asked if you want to change the
sources.list file. If you've previously
configured the file, you should respond
No. If
you've not configured the file, you can respond
Yes, which initiates a dialog that builds a
simple configuration. Here's a sample dialog that shows the responses
you should give to install packages from the CD-ROM diskette that
accompanies this book:
I see you already have a source list.
-------------------------------------------------------
source list displayed here: contents vary
-------------------------------------------------------
Do you wish to change it?[y/N]
y
Set up a list of distribution source locations
Please give the base URL of the debian distribution.
The access schemes I know about are: http ftp file
For example:
file:/mnt/debian,
ftp://ftp.debian.org/debian,
https://ftp.de.debian.org/debian,
URL [https://http.us.debian.org/debian]:
file:/cdrom
Please give the distribution tag to get or a path to the
package file ending in a /. The distribution
tags are typically something like: stable unstable frozen non-US
Distribution [stable]:
stable
Please give the components to get
The components are typically something like: main contrib non-free
Components [main contrib non-free]:
main contrib
Would you like to add another source?[y/N]
N
The sample dialog assumes that you CD-ROM has been mounted as
/cdrom. If your CD-ROM is mounted differently,
you'll need to revise the dialog.
After
dselect records your choice of access
method, the main menu screen re-appears.
After selecting the access method, you should instruct
dselect to update information on available
packages. To do so, use the arrow keys to highlight the Update menu
item and press
Enter. After a short
time, the main menu will re-appear.
Once you've updated the information on available packages,
you're ready to select packages for installation or removal. To do so,
use the arrow keys to highlight the Select menu item and press
Enter. The screen shown in
Figure C.4 appears.
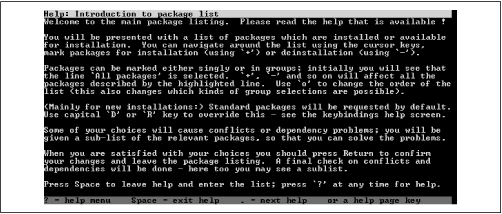
This screen provides an overview of the package selection
screens. When you've read its contents, press
Space to go to the package selection screen,
which is shown in
Figure C.5.
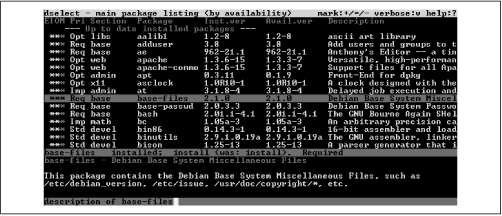
To use the package selection screen, use the arrow keys to
highlight a package in the upper part of the screen. The lower part of
the screen will display information about the highlighted package. To
select the package for installation, press
+; to select an installed package for removal,
press
-.
You can search the package database by typing a slash
(/) followed by the string for which you wish to
search. To find successive instances of the same string, type a
backslash (\). For example, to find the first package that contains
the string
gnome in its name or description, type
/gnome and press
Enter.
If you select for installation a package that requires one or
more other packages that are not installed, a dependency conflict
results. Similarly, a dependency conflict results if you mark for
removal a package required by an installed package or if you mark for
installation a package that conflicts with an installed package. When
dselect detects a dependency conflict, it presents
the screen shown in
Figure C.6.
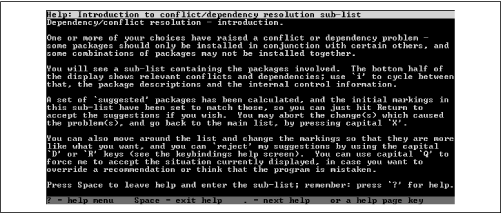
The same screen appears if you select for installation a package
that specifies recommended or suggested packages to be installed with
it. A recommended package is one that most users install with the
recommending package. A suggested package is one that is related to
the suggesting package; suggested packages often extend or complement
the functionality of the suggesting package.
When you press
Space, you're
presented with the conflict resolution screen, shown in
Figure C.7. This screen lets you quickly select
packages for installation or removal the packages involved in a
dependency conflict. The screen also presents default choices for
recommended and suggested packages.
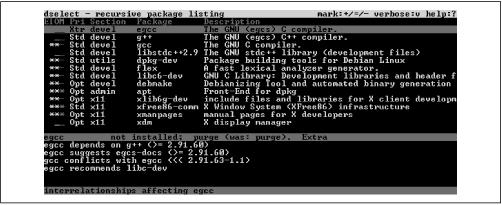
Using the arrow keys to highlight an entry lets you view a list
of dependencies related to the entry. By pressing
+ or
- you
can select packages for installation or removal, just as on the
selection screen. When you're done working out dependencies, you can
press
Space to return to the selection
screen.
You can select the Select function in any of several
ways. Pressing
Space returns you to the
main menu, where you can initiate installation or removal of
packages. Pressing
x cancels your
selections and returns you to the main menu. This feature is useful if
you change your mind about installing a package, possibly owing to
conflicts associated with the package.
To begin installing the selected packages, use the arrow keys to
highlight the Install menu item and press
Enter. As packages are downloaded or installed,
you'll see messages on the screen.
If you're using the
apt access method,
selecting Install actually initiates installation, removal, and
configuration of packages. You can exit
dselect
after the installation process completes.
If you're using some other access method,
dselect may not install every selected package in a
single operation. When the installation process completes, you should
select Install and see if more packages are installed. When you select
Install and no more packages are installed, you can proceed to the
subsequent steps: configuration and removal.
When the installation process is complete,
dselect prompts you to press
Enter to return to the main menu.
To begin configuring the installed packages, use the arrow keys
to highlight the Configure menu item and press
Enter. Packages that require configuration will
prompt you for configuration choices. When the configuration process
is complete,
dselect prompts you to press
Enter to return to the main menu.
To begin removing the packages selected for removal, use the
arrow keys to highlight the Remove menu item and press
Enter. When the removal process is complete,
dselect prompts you to press
Enter to return to the main menu.
To exit
dselect, use the arrow keys to
highlight the Quit menu item and press
Enter.
