Administering Kerberos Policies
This section provides step-by-step instructions used to administer policies with the SEAM Tool.
This section also provides examples of command-line equivalents, when available.
Administering Kerberos Policies (Task Map)
Task |
Description |
For Instructions |
|---|
View the list
of policies. |
View the list of policies by clicking the Policies tab. |
How to View the List of Kerberos Policies |
View a
policy's attributes. |
View a policy's attributes by selecting the policy in the Policy
List, then clicking the Modify button. |
How to View a Kerberos Policy's Attributes |
Create a new policy. |
Create a new policy by
clicking the Create New button in the Policy List panel. |
How to Create a New Kerberos Policy |
Duplicate a policy. |
Duplicate a
policy by selecting the policy to duplicate in the Policy List, then clicking
the Duplicate button. |
How to Duplicate a Kerberos Policy |
Modify a policy. |
Modify a policy by selecting the policy to
modify in the Policy List, then clicking the Modify button. Note that you cannot
modify a policy's name. To rename a policy, you must duplicate the policy,
specify a new name for it, save it, and then delete the old
policy. |
How to Modify a Kerberos Policy |
Delete a policy. |
Delete a policy by selecting the policy to delete in
the Policy List, then clicking the Delete button. |
How to Delete a Kerberos Policy |
How to View the List of Kerberos Policies
An example of the command-line equivalent follows this procedure.
- If necessary, start the SEAM Tool.
See How to Start the SEAM Tool for more information.
$ /usr/sbin/gkadmin
- Click the Policies tab.
The list of policies is displayed.
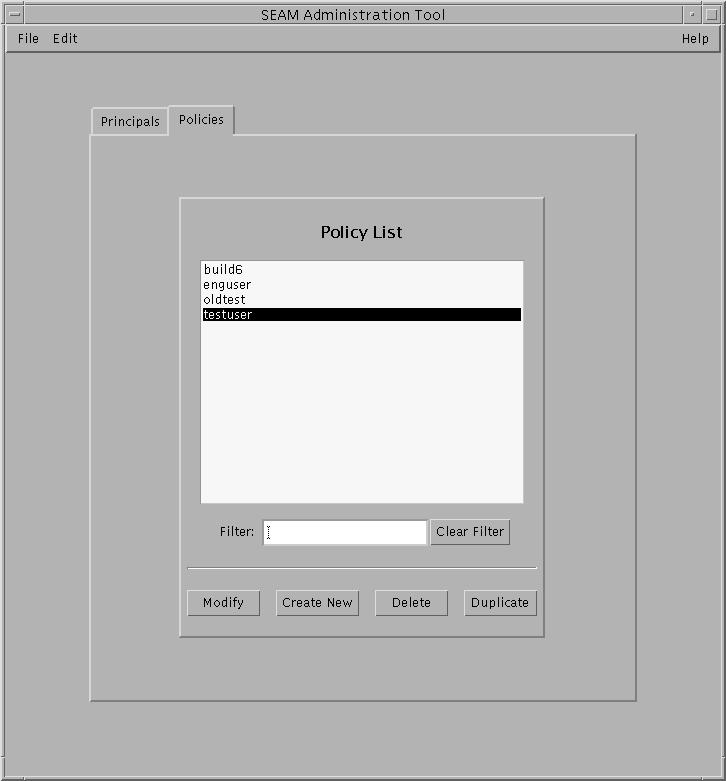
- Display a specific policy or a sublist of policies.
Type a filter string in the Filter field, and press Return. If the
filter succeeds, the list of policies that match the filter is displayed.
The filter string must consist of one or more characters. Because the filter
mechanism is case sensitive, you need to use the appropriate uppercase and lowercase
letters for the filter. For example, if you type the filter string ge,
the filter mechanism displays only the policies with the ge string in them
(for example, george or edge).
If you want to display the entire list of policies, click Clear
Filter.
Example 25-9 Viewing the List of Kerberos Policies (Command Line)
In the following example, the list_policies command of kadmin is used to list
all the policies that match *user*. Wildcards can be used with the
list_policies command.
kadmin: list_policies *user*
testuser
enguser
kadmin: quit
How to View a Kerberos Policy's Attributes
An example of the command-line equivalent follows this procedure.
- If necessary, start the SEAM Tool.
See How to Start the SEAM Tool for more information.
$ /usr/sbin/gkadmin
- Click the Policies tab.
- Select the policy in the list that you want to view, then click
Modify.
The Policy Details panel is displayed.
- When you are finished viewing, click Cancel.
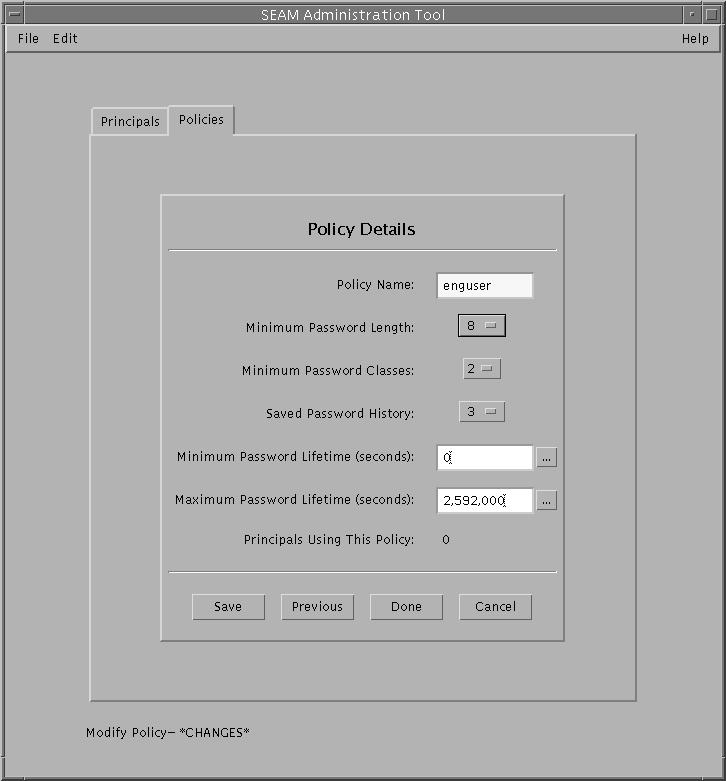
Example 25-10 Viewing a Kerberos Policy's Attributes
The following example shows the Policy Details panel when you are viewing the
test policy.
Example 25-11 Viewing a Kerberos Policy's Attributes (Command Line)
In the following example, the get_policy command of kadmin is used to view
the attributes of the enguser policy.
kadmin: get_policy enguser
Policy: enguser
Maximum password life: 2592000
Minimum password life: 0
Minimum password length: 8
Minimum number of password character classes: 2
Number of old keys kept: 3
Reference count: 0
kadmin: quit
The Reference count is the number of principals that use this policy.
How to Create a New Kerberos Policy
An example of the command-line equivalent follows this procedure.
- If necessary, start the SEAM Tool.
See How to Start the SEAM Tool for more information.
$ /usr/sbin/gkadmin
- Click the Policies tab.
- Click New.
The Policy Details panel is displayed.
- Specify a name for the policy in the Policy Name field.
The policy name is mandatory.
- Specify values for the policy's attributes.
Choose Context-Sensitive Help from the Help menu for information about the various attributes
in this window. Or, go to Table 25-5 for all the policy attribute descriptions.
- Click Save to save the policy, or click Done.
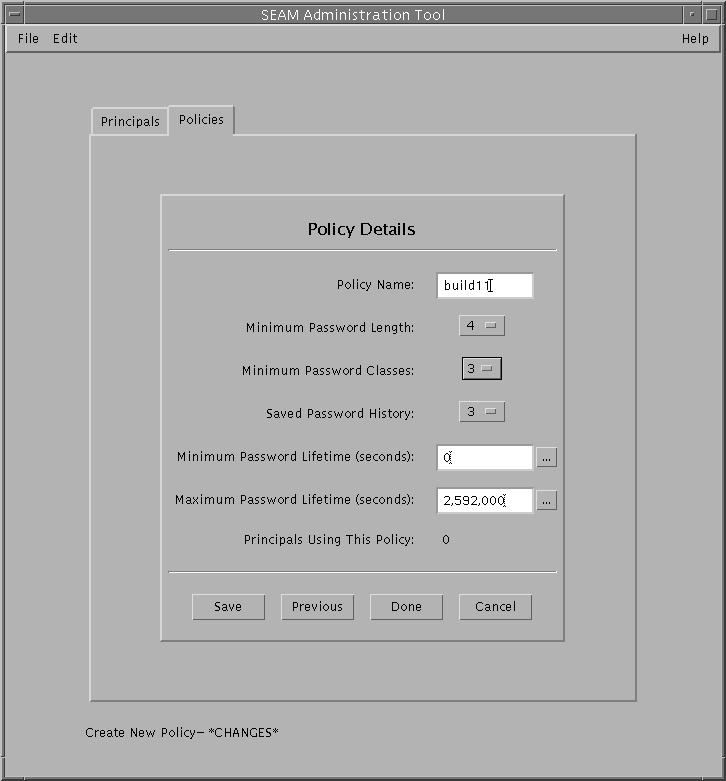
Example 25-12 Creating a New Kerberos Policy
In the following example, a new policy called build11 is created. The Minimum
Password Classes is set to 3.
Example 25-13 Creating a New Kerberos Policy (Command Line)
In the following example, the add_policy command of kadmin is used to create
the build11 policy. This policy requires at least 3 character classes in a
password.
$ kadmin
kadmin: add_policy -minclasses 3 build11
kadmin: quit
How to Duplicate a Kerberos Policy
This procedure explains how to use all or some of the attributes
of an existing policy to create a new policy. No command-line equivalent exists for
this procedure.
- If necessary, start the SEAM Tool.
See How to Start the SEAM Tool for more information.
$ /usr/sbin/gkadmin
- Click the Policies tab.
- Select the policy in the list that you want to duplicate, then click
Duplicate.
The Policy Details panel is displayed. All the attributes of the selected policy
are duplicated, except for the Policy Name field, which is empty.
- Specify a name for the duplicated policy in the Policy Name field.
The policy name is mandatory. To make an exact duplicate of the policy
you selected, skip to Step 6.
- Specify different values for the policy's attributes.
Choose Context-Sensitive Help from the Help menu for information about the various attributes
in this window. Or, go to Table 25-5 for all the policy attribute descriptions.
- Click Save to save the policy, or click Done.
How to Modify a Kerberos Policy
An example of the command-line equivalent follows this procedure.
- If necessary, start the SEAM Tool.
See How to Start the SEAM Tool for details.
$ /usr/sbin/gkadmin
- Click the Policies tab.
- Select the policy in the list that you want to modify, then click
Modify.
The Policy Details panel is displayed.
- Modify the policy's attributes.
Choose Context-Sensitive Help from the Help menu for information about the various attributes
in this window. Or, go to Table 25-5 for all the policy attribute descriptions.
Note - You cannot modify a policy's name. To rename a policy, you must duplicate
the policy, specify a new name for it, save it, and then
delete the old policy.
- Click Save to save the policy, or click Done.
Example 25-14 Modifying a Kerberos Policy (Command Line)
In the following example, the modify_policy command of kadmin is used to modify
the minimum length of a password to five characters for the build11 policy.
$ kadmin
kadmin: modify_policy -minlength 5 build11
kadmin: quit
How to Delete a Kerberos Policy
An example of the command-line equivalent follows this procedure.
Note - Before you delete a policy, you must cancel the policy from all principals
that are currently using it. To do so, you need to modify
the principals' Policy attribute. The policy cannot be deleted if any principal is
using it.
- If necessary, start the SEAM Tool.
See How to Start the SEAM Tool for more information.
$ /usr/sbin/gkadmin
- Click the Policies tab.
- Select the policy in the list that you want to delete, then click
Delete.
After you confirm the deletion, the policy is deleted.
Example 25-15 Deleting a Kerberos Policy (Command Line)
In the following example, the delete_policy command of the kadmin command is used
to delete the build11 policy.
kadmin: delete_policy build11
Are you sure you want to delete the policy "build11"? (yes/no): yes
kadmin: quit
Before you delete a policy, you must cancel the policy from all
principals that are currently using it. To do so, you need to use
the modify_principal -policy command of kadmin on the affected principals. The delete_policy command fails
if the policy is in use by a principal.
